Problem Statement: To design, build, and deploy an autonomous RC car capable of mapping, localizing, and navigating real-world environments using LiDAR-based SLAM.
Tools: ROS2 (Humble), Python, C++, LiDAR, IMU, Wheel Encoders, Raspberry Pi, Arduino, Ubuntu, RViz
Concepts: LiDAR-based SLAM, Localization, Sensor Fusion, Path Planning, Autonomous Navigation, State Estimation, Real-time System Integration
To
December 2025
From
August 2025
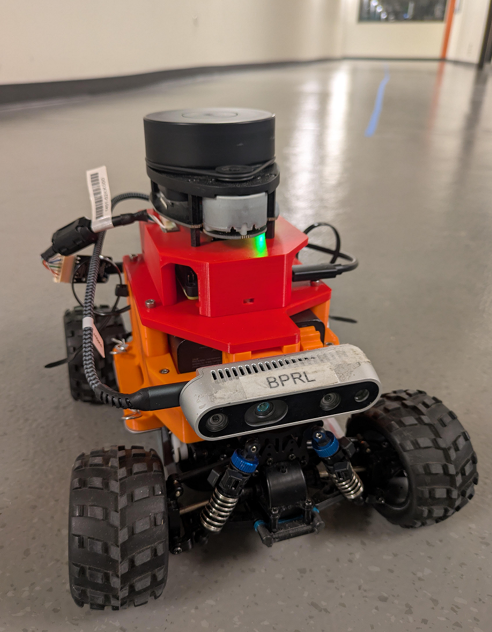
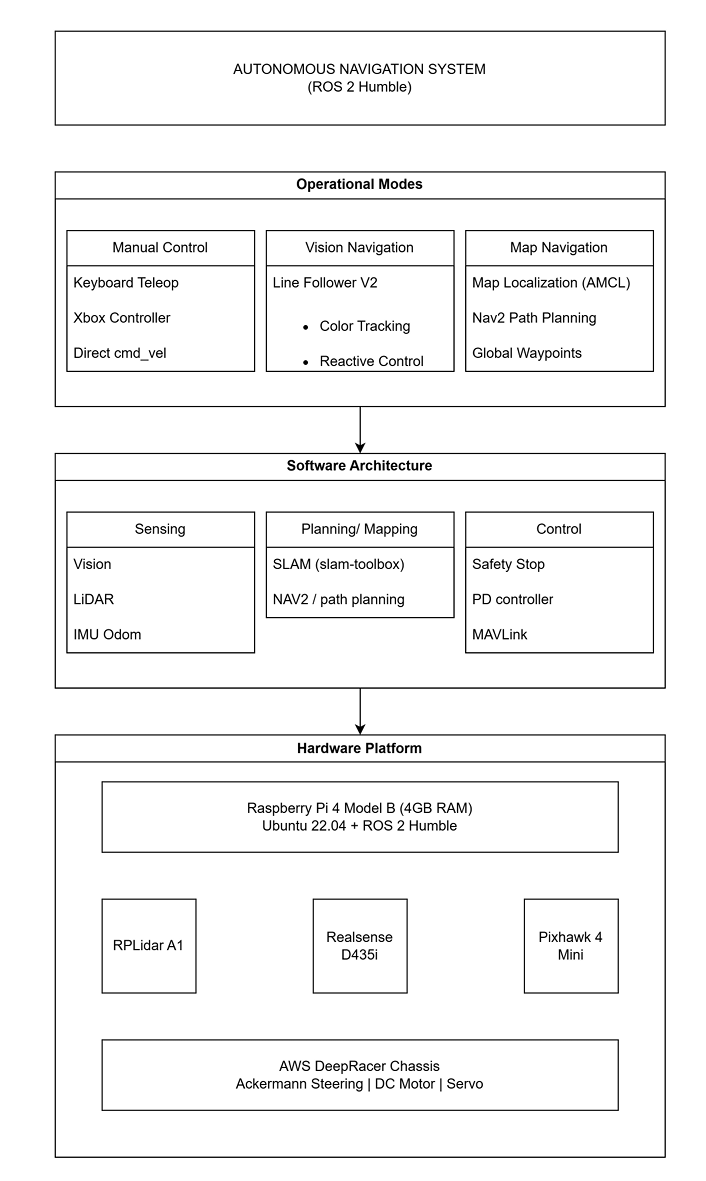
Designed and deployed a fully autonomous indoor RC vehicle for competitive time-trial navigation using ROS2 Humble on an AWS DeepRacer platform, with a focus on reliability and repeatability under real-world constraints.
Developed a dual-mode navigation architecture that seamlessly switched between vision-based tape following and LiDAR-based SLAM to ensure robust operation across different course conditions.
Integrated a 360° RP-LiDAR A1 and Intel RealSense D435i RGB-D camera, enabling complementary perception for mapping, localization, obstacle awareness, and visual navigation.
Implemented a modular ROS2 node architecture covering sensing, mapping, localization, planning, and control, with standardized topics and clean separation of responsibilities.
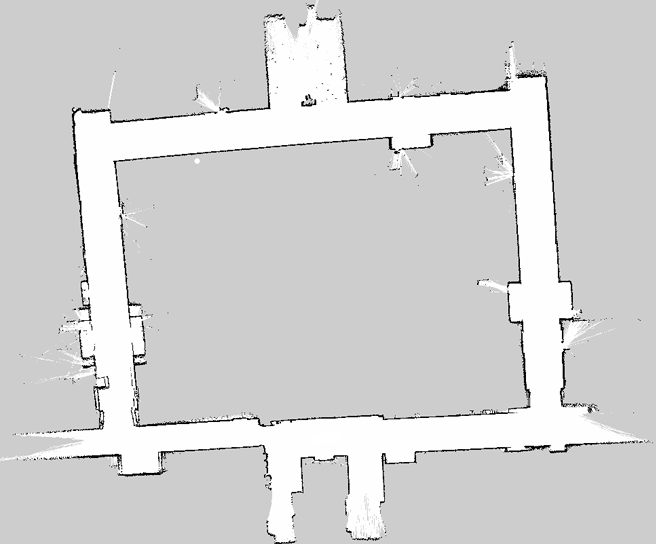
Performed real-time 2D SLAM using slam_toolbox, generating consistent occupancy grid maps with loop closure and pose-graph optimization to minimize long-term drift.
Enabled global localization using AMCL, anchoring wheel odometry to a static map and maintaining accurate pose estimates across repeated autonomous laps.
Configured the Nav2 navigation stack for global path planning, local trajectory optimization, collision avoidance, and recovery behaviors in dynamic indoor environments.
Designed a custom OpenCV-based blue tape detection pipeline, using HSV thresholding and image preprocessing to robustly identify track boundaries under varying lighting conditions.
Implemented a bird’s-eye-view (BEV) transform to normalize perspective distortion and allow consistent line detection independent of distance from the camera.
Developed a PD-controlled line-following algorithm that converted visual centroid error into smooth steering commands for reactive navigation.
Built a waypoint-driven autonomous navigation system, enabling the robot to complete full laps using only a prebuilt SLAM map and real-time sensor feedback.
Integrated a Pixhawk flight controller via MAVLink, separating low-level motor control from high-level autonomy to improve stability and control responsiveness.
Validated system performance through timed trials, achieving collision-free autonomous laps with consistent localization accuracy and repeatable behavior.